The Mediterranean diet is often touted as one of the healthiest diets in the world, known for its emphasis on fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. However, there is some confusion regarding whether or not dairy is included in this popular diet. While some people believe that dairy is a staple of the Mediterranean diet, others argue that it is not necessary for a healthy diet.
Those who believe that dairy is an important part of the Mediterranean diet point to the fact that many traditional Mediterranean dishes include cheese and yogurt. For example, feta cheese is a common ingredient in Greek salads, while tzatziki sauce is made from yogurt and cucumbers. Additionally, some advocates of the Mediterranean diet argue that dairy can provide important nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D.
On the other hand, some experts argue that dairy is not a necessary component of the Mediterranean diet. They point out that many traditional Mediterranean dishes, such as hummus and tabbouleh, are completely dairy-free. Furthermore, some studies have suggested that excessive dairy consumption may be linked to health issues such as heart disease and certain types of cancer. Ultimately, whether or not dairy is included in the Mediterranean diet is a matter of personal preference and dietary needs.
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is a popular diet that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients. This diet is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. The Mediterranean diet is known for its health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
The Mediterranean diet is based on the following principles:
- Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds
- Consuming fish and seafood at least twice a week
- Limiting red meat consumption and replacing it with poultry or plant-based proteins
- Using healthy fats, such as olive oil, instead of butter or other animal fats
- Enjoying dairy products in moderation, such as yogurt and cheese
- Drinking red wine in moderation, if desired
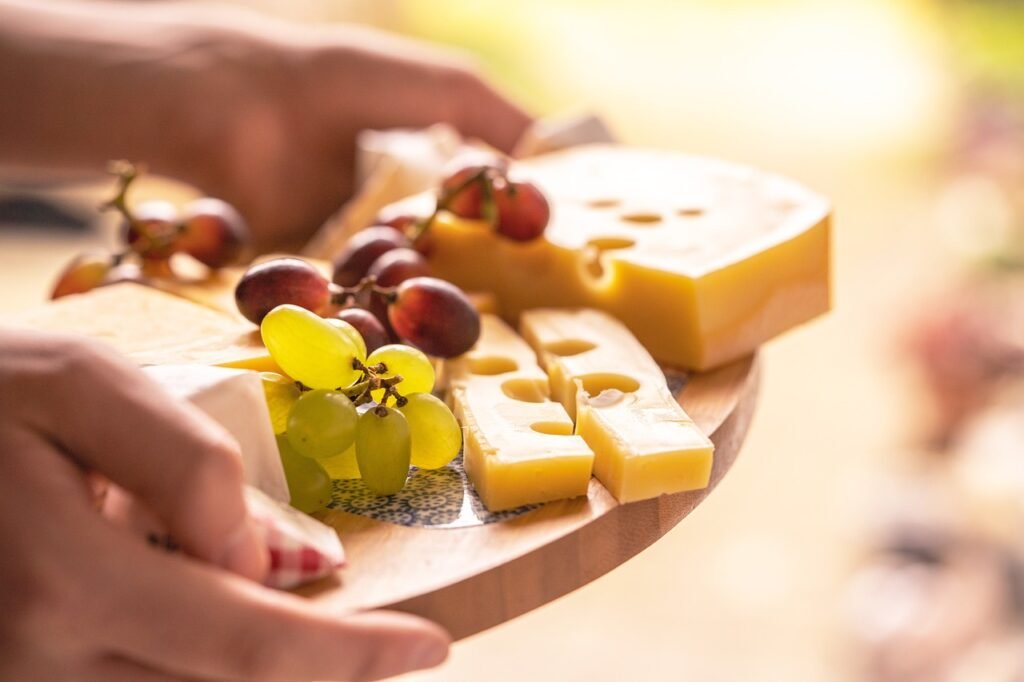
While the Mediterranean diet does include dairy products, they are consumed in moderation. Dairy products such as yogurt and cheese are rich in nutrients such as calcium, protein, and vitamin D. However, excessive consumption of dairy products can lead to health problems such as high cholesterol and increased risk of heart disease.
In summary, the Mediterranean diet is a healthy and balanced diet that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods. While it does include dairy products, they are consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Dairy in the Mediterranean Diet
Role of Dairy
Even though dairy is not a staple food in the Mediterranean diet, it is consumed in moderate amounts. Dairy products are an excellent source of calcium, which is essential for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. Calcium also plays a vital role in muscle function, nerve transmission, and blood clotting. Dairy products are also rich in protein, which is necessary for building and repairing tissues, and for maintaining a healthy immune system.
Common Dairy Foods
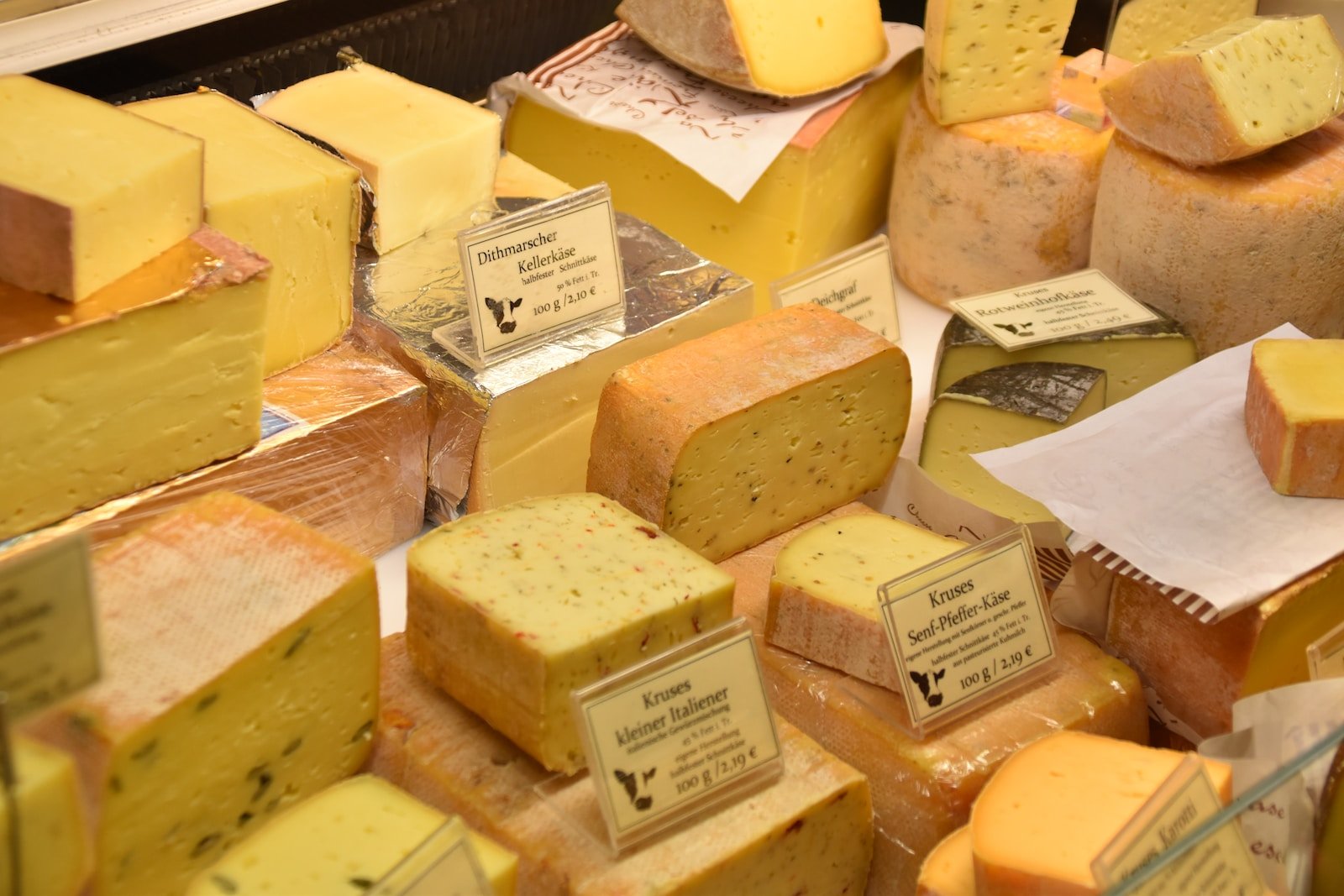
The most common dairy foods in the Mediterranean diet include cheese, yogurt, and milk. Cheese is often used as a condiment or garnish, rather than as a main ingredient. Feta cheese, which is made from sheep or goat milk, is popular in the Mediterranean diet.
Yogurt is a staple food in the Mediterranean diet and is often consumed as a snack or as a dessert. Greek yogurt, which is thicker and creamier than regular yogurt, is a popular type of yogurt in the Mediterranean region.
Milk is also consumed in moderate amounts in the Mediterranean diet. It is often used in cooking or as a base for sauces and soups.
Health Benefits of Dairy in the Mediterranean Diet
Nutritional Value
Dairy provides an array of essential nutrients that are beneficial for overall health. Milk and dairy products are excellent sources of calcium, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. In addition to calcium, dairy products also contain other important nutrients such as vitamin D, vitamin B12, and potassium.
Impact on Heart Health
Research has shown that consuming dairy products as part of a healthy diet can have a positive impact on heart health. Studies have found that consuming low-fat dairy products can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. Dairy products are also a good source of protein, which can help with weight management and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
In addition to the nutritional benefits, dairy products can provide probiotics, beneficial bacteria that contribute to better gut health. Yogurt, especially, contains probiotics, offering numerous health benefits and can help with digestion and boost the immune system.
Overall, dairy products can provide a range of health benefits. It is important to choose low-fat or non-fat dairy products to ensure that you are getting the nutritional benefits without the added saturated fat.
Possible Concerns with Dairy
While dairy can be a great source of nutrients, some people may have concerns about including it in their diet. Here are a few potential issues to keep in mind:
Lactose Intolerance
One of the most common concerns with dairy is lactose intolerance. This condition occurs when the body is unable to digest the lactose sugar found in milk and other dairy products. Symptoms can include bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
However, it’s important to note that not all people with lactose intolerance need to avoid dairy entirely. Many can tolerate small amounts of lactose without any issues. Additionally, there are lactose-free dairy products available, such as lactose-free milk and cheese.
High-Fat Content
Dairy products can also be high in fat, which may be a concern for some people. While the Mediterranean diet does include some high-fat dairy products such as cheese and yogurt, it also emphasizes low-fat options such as skim milk and reduced-fat cheese.
Environmental Concerns
Some people may choose to avoid dairy for environmental reasons. The dairy industry can have a significant impact on the environment, including greenhouse gas emissions and water usage. However, it’s worth noting that not all dairy production methods are created equal. Some dairy farmers prioritize sustainability and environmental stewardship and may use practices such as rotational grazing to minimize their impact.
Overall, while there are some potential concerns with including dairy in the Mediterranean diet, many people find that it can be a healthy and delicious addition to their meals. As with any dietary choice, it’s important to consider your individual needs and preferences when deciding whether or not to include dairy in your diet.
Alternatives to Dairy in the Mediterranean Diet
While dairy is a common component of the Mediterranean diet, it is not necessary to consume it to follow the diet. Many alternatives to dairy can provide similar nutritional benefits.
One popular alternative is plant-based milk, such as almond, soy, or oat milk. These milk alternatives are often fortified with calcium and vitamin D, which are important nutrients found in dairy products. They also tend to be lower in calories and fat than dairy milk.
Another alternative is to consume more nuts and seeds, which are rich in calcium and other nutrients. For example, a serving of almonds contains about 75mg of calcium, which is about 7% of the daily recommended intake. Sesame seeds are also a good source of calcium, with one tablespoon providing about 9% of the daily recommended intake.
Leafy green vegetables, such as kale, spinach, and collard greens, are also high in calcium and other important nutrients. One cup of cooked kale contains about 94mg of calcium, which is about 9% of the daily recommended intake.
Finally, fermented foods, such as sauerkraut and kimchi, can provide probiotics, which are beneficial for gut health. Yogurt is a common source of probiotics in the Mediterranean diet, but fermented vegetables can be a good alternative for those who do not consume dairy.
Overall, many alternatives to dairy can be included in the Mediterranean diet. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, individuals can meet their nutritional needs without consuming dairy products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet is a plant-based diet that promotes nutrient-dense foods. While dairy is not a central component of the Mediterranean diet, it is still consumed in moderation by some people who follow this eating pattern.
It is important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to the Mediterranean diet, and some people may choose to include more or less dairy in their diet depending on their individual preferences and needs. Additionally, some studies have suggested that consuming dairy products may have health benefits, such as improving bone health and reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases.
Overall, the Mediterranean diet is a flexible and balanced eating pattern that can be adapted to meet the needs and preferences of different individuals. Whether or not to include dairy in the diet is a personal choice that should be based on individual needs and preferences.