Pregnancy is a critical period for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. A balanced and healthy diet is essential during this time to ensure that the mother and the baby get all the necessary nutrients. One diet that has gained popularity in recent years is the Mediterranean diet.
Studies have shown that following a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy can have numerous benefits for both the mother and the baby. It can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes, preterm birth, and low birth weight. It can also improve the baby’s brain development and reduce the risk of allergies and asthma.
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is a plant-based diet that emphasizes the consumption of vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, and seeds. It also includes moderate amounts of fish and poultry, while limiting red meat and processed foods. This diet is rich in healthy fats, such as olive oil, and encourages the use of herbs and spices for replacing salt to flavor foods.
Key Components
The Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional dietary patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Spain, Italy, and Greece. The key components of this diet include:
- Fruits and vegetables: These are the foundation of the Mediterranean diet and should be consumed in abundance.
- Whole grains: These are an excellent source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Legumes: These include beans, lentils, and chickpeas, which are a good source of protein and fiber.
- Nuts and seeds: These are a great source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Fish and poultry: These are the primary sources of protein in the Mediterranean diet.
- Olive oil: This is the main source of fat in the Mediterranean diet and is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Herbs and spices: These are used to flavor foods instead of salt.
Health Benefits
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of heart disease: The Mediterranean diet is rich in healthy fats, which can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Improved cognitive function: Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet may help improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Lower risk of certain cancers: The high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in the Mediterranean diet may help lower the risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast and colon cancer.
- Improved gut health: The Mediterranean diet is rich in fiber, which can help improve gut health and reduce the risk of digestive problems.
- Weight loss: The Mediterranean diet offers a healthful and sustainable approach to weight loss by prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods while discouraging the consumption of processed foods.
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet is a healthy and sustainable way of eating that has numerous health benefits. By prioritizing nutrient-dense, whole foods and limiting processed foods, the Mediterranean diet can help improve heart health, cognitive function, and gut health, while also promoting weight loss.
Mediterranean Diet During Pregnancy
Nutritional Needs
A Mediterranean diet during pregnancy can provide essential nutrients for both the mother and the growing fetus. This diet is rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, which can help meet the increased nutritional needs of pregnant women.
The following table provides an overview of the key nutrients found in a Mediterranean diet and their benefits during pregnancy:
| Nutrient | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Folate | Helps prevent birth defects and supports the development of the nervous system |
| Iron | Supports the formation of red blood cells and prevents anemia |
| Calcium | Builds strong bones and teeth in the developing fetus |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Supports brain and eye development in the fetus |
| Vitamin D | Helps the body absorb calcium and supports fetal bone growth |
Safe Foods
A Mediterranean diet during pregnancy can also include a variety of safe and healthy foods. However, it’s important to avoid certain foods that can pose a risk to the developing fetus.
The following table provides an overview of safe and unsafe foods during pregnancy:
| Safe Foods | Unsafe Foods |
|---|---|
| Fruits and vegetables | Raw or undercooked meat and eggs |
| Whole grains | Unpasteurized dairy products |
| Lean proteins (e.g. fish, chicken, beans) | Raw or undercooked fish |
| Healthy fats (e.g. olive oil, nuts, seeds) | Processed foods high in sugar and salt |
| Low-fat dairy products | Alcohol |
Overall, a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy can provide essential nutrients for both the mother and the growing fetus. It’s important to choose a variety of foods and avoid foods that can pose a risk to the developing fetus.
Meal Planning and Preparation
Pregnancy is a time when it is essential to maintain a healthy diet to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. The Mediterranean diet is a great choice for pregnant women as it is rich in nutrients, fiber, and healthy fats. Proper meal planning and preparation can make it easier to follow the Mediterranean diet during pregnancy.
Sample Meal Plan
Here is a sample meal plan for a day on the Mediterranean diet during pregnancy:
Breakfast
- Greek yogurt with honey and mixed berries
- Whole-grain toast with avocado and tomato
- Decaf tea or coffee
Snack
- Apple slices with almond butter
Lunch
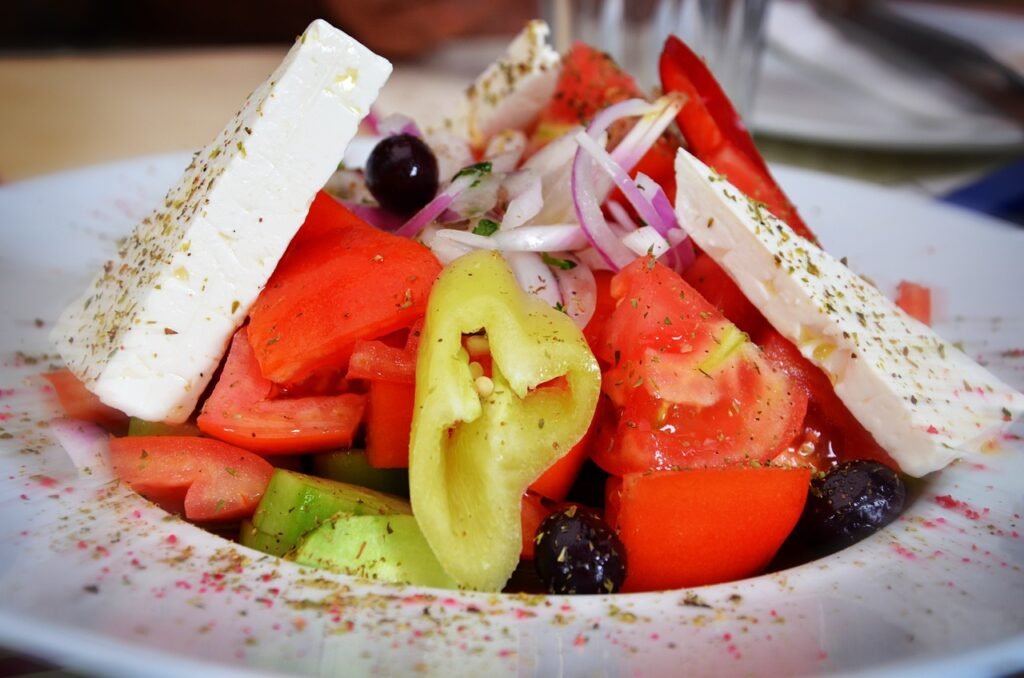
- Greek salad with feta cheese, olives, cucumber, and tomatoes
- Whole-grain pita bread
- Hummus
Snack
- Carrots and celery with tzatziki
Dinner
- Grilled salmon with lemon and dill
- Roasted vegetables (e.g., zucchini, bell peppers, and onions)
- Quinoa
Dessert
- Fresh fruit salad
Easy Mediterranean Recipes
Preparing Mediterranean meals during pregnancy can be simple and delicious. Here are a few easy recipes to try:
Greek Salad
- Cut up cucumbers, tomatoes, and bell peppers into bite-sized pieces.
- Add kalamata olives and feta cheese.
- Dress with olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper.
Hummus
- Combine one can of chickpeas (drained and rinsed), 1/4 cup of tahini, 2 tablespoons of olive oil, 2 cloves of garlic, and 2 tablespoons of lemon juice in a food processor.
- Blend until smooth.
- Add salt and pepper to taste.
Grilled Salmon
- Preheat the grill to medium-high heat.
- Season salmon fillets with lemon juice, dill, salt, and pepper.
- Grill for 4-6 minutes on each side or until cooked through.
By following a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy and utilizing simple meal planning and preparation techniques, pregnant women can ensure they are consuming a nutritious and balanced diet for themselves and their growing babies.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Dealing with Cravings
One of the potential challenges of following a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy is dealing with cravings. Pregnant women may experience strong cravings for certain foods that are not typically part of the Mediterranean diet, such as sweets, salty snacks, or fast food.
To address this challenge, it’s important to understand the underlying reasons behind the cravings. For example, cravings for sweets may be due to low blood sugar levels, while cravings for salty foods may be due to dehydration. Eating regular meals and snacks that include a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings.
It’s also important to find healthy alternatives to satisfy cravings. For example, instead of reaching for a candy bar, a pregnant woman could have a piece of fruit with a handful of nuts or a small serving of dark chocolate. If a pregnant woman is craving something salty, she could opt for a small serving of olives or pickles.
Maintaining Variety
Another potential challenge of following a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy is maintaining variety. Pregnant women may feel like they are eating the same foods over and over again, which can lead to boredom and a lack of motivation to stick to the diet.
To address this challenge, pregnant women can experiment with different recipes and cooking methods to add variety to their meals. For example, they could try grilling vegetables instead of roasting them or adding different herbs and spices to their meals.
It’s also important to incorporate a variety of foods from each food group. For example, pregnant women could try different types of fish, such as salmon, tuna, or sardines, or different types of whole grains, such as quinoa, brown rice, or bulgur.
By being creative and experimenting with different foods and cooking methods, pregnant women can maintain variety in their diet and continue to enjoy the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
Before starting any new diet or exercise regimen during pregnancy, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. This is especially true for the Mediterranean diet, as it may not be appropriate for everyone.
A healthcare professional can help determine if the Mediterranean diet is a safe and healthy option for a pregnant woman. They can also provide guidance on how to properly follow the diet and ensure that all nutritional needs are being met.
It is important to note that the Mediterranean diet is not a substitute for prenatal vitamins or other necessary supplements. A healthcare professional can help determine which supplements are necessary and provide recommendations on dosage and timing.
Additionally, if a pregnant woman has any pre-existing medical conditions or complications, a healthcare professional can help determine if the Mediterranean diet is appropriate or if modifications need to be made.
Overall, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting the Mediterranean diet during pregnancy is crucial for ensuring the health and safety of both the mother and the baby.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet is a healthy and nutritious way for pregnant women to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of gestational diabetes and other pregnancy complications. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, pregnant women can ensure that they are providing their bodies and their growing babies with the essential nutrients they need.
In addition to its nutritional benefits, the Mediterranean diet is also a sustainable and environmentally-friendly way of eating. By choosing locally-sourced, seasonal foods and reducing the consumption of processed and packaged foods, pregnant women can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier planet.
It is important to note that while the Mediterranean diet can be a healthy choice for pregnant women, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Every woman’s nutritional needs are different, and it is important to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to ensure that individual needs are being met.
Overall, the Mediterranean diet is a delicious and satisfying way for pregnant women to nourish themselves and their growing babies. By incorporating a variety of whole, plant-based foods and healthy fats, pregnant women can enjoy a balanced and nutritious diet that supports optimal health and well-being.